Vietnam is an emerging economy experiencing a strong consumer boom. The impacts of consumer-related pollution are becoming increasingly apparent, particularly packaging pollution at the end of the product lifecycle. The legal framework related to packaging management is gradually being improved and made more rigorous, clearly defining environmental protection obligations: Who is responsible for discarded packaging? What are their obligations under the law?
Packaging waste – a serious environmental issue in Vietnam
Packaging waste is becoming one of the most pressing environmental issues in Vietnam. According to the World Bank, Vietnam generates approximately 3.9 million tons of plastic waste annually, with packaging accounting for a large portion, but only 10-15% is collected and recycled. The remaining discarded packaging is not properly disposed of, causing serious environmental pollution. Therefore, legislation is needed to manage packaging waste more effectively.
The first environmental legal grounds for packaging
In Vietnam, the 2020 Environmental Protection Law for the first time stipulated that economic entities such as manufacturers and importers must recycle packaging materials that have been introduced into the market at a reasonable rate and according to appropriate specifications. This was followed by more detailed regulations aimed at realizing the provisions of the Environmental Protection Law.
The law is based on the “polluter pays” principle. Manufacturers and importers of packaged products are economic actors responsible for bringing packaging along with the product into social circulation, and are also economic beneficiaries of the product circulation process. Therefore, they are also responsible for complying with legal regulations regarding the Extended Liability of Manufacturers and Importers of Packaged Products.
What is the Extended Producer Responsibility for packaged products manufacturers and importers?
The responsibility of manufacturers and importers for a product extends to the period after it has been consumed. What remains of the product after its original intended value is gone remains the responsibility of the manufacturer or importer, even after ownership has transferred to the end consumer. Remaining components, including product packaging, are expected to be collected and sorted before disposal. The usual disposal method is reuse and recycling of the packaging.
How are legal entities fulfilling this legal responsibility?
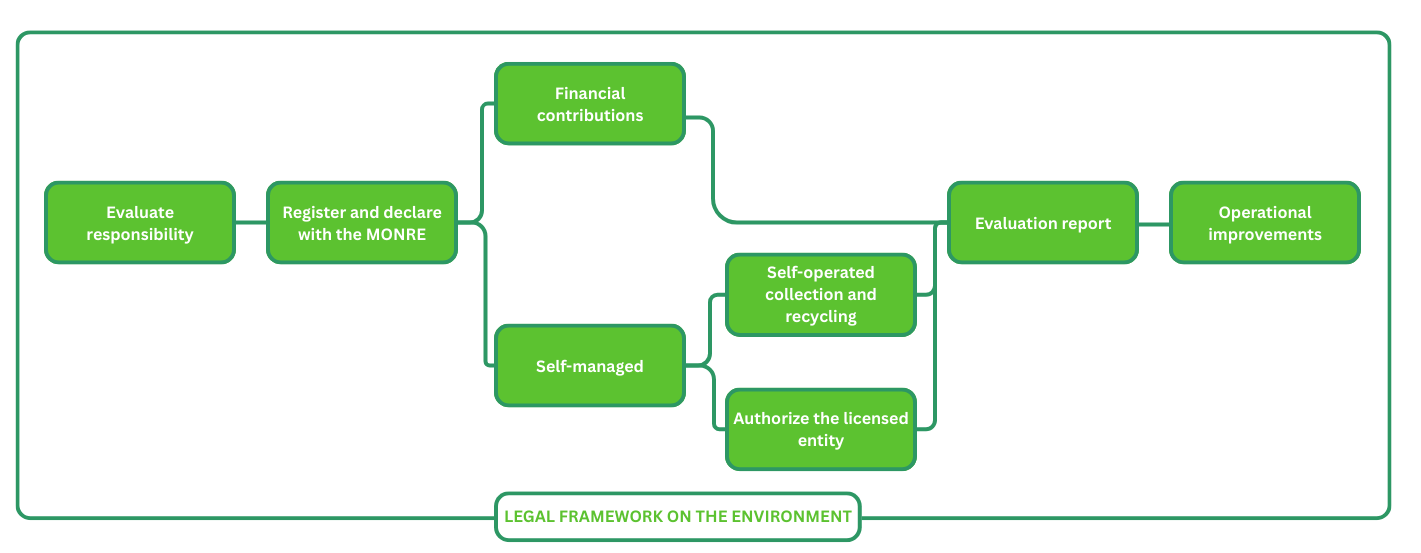 Figure 1. Implementation roadmap for Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) for packaged products manufacturers and importers
Figure 1. Implementation roadmap for Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) for packaged products manufacturers and importers
Future legal requirements for Vietnam
In the future, to reduce the negative environmental impacts of packaging, Vietnam aims to introduce clearer policies on the import, production, and consumption of packaging domestically. The legal framework will be increasingly strengthened, helping manufacturers and importers to be more transparent about their responsibilities and obligations. Organizations, individuals, and businesses will be regulated and encouraged to design, collect, sort waste at source, and effectively process packaging waste… This will create a synchronized effort to build a healthier living environment in the future.
REFERENCES
National Assembly of Vietnam. (2020). Law No. 72/2020/QH14 of the National Assembly: Law on Environmental Protection


 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt 日本語
日本語