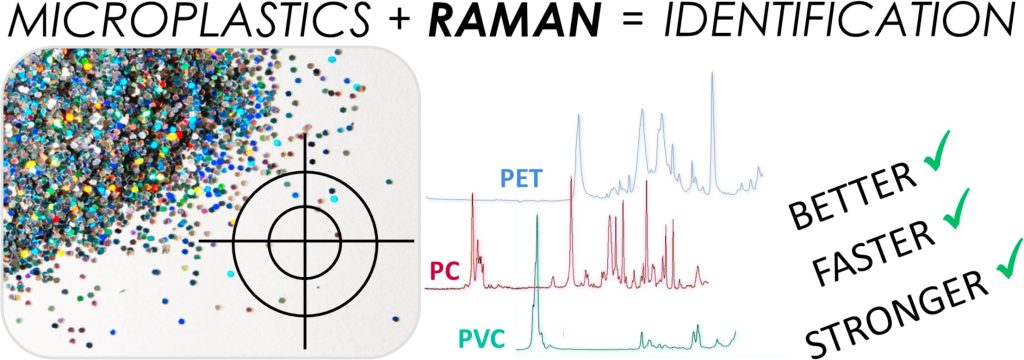
Raman spectroscopy is a non-destructive technique that provides detailed information about the chemical structure, phase and polymorph, crystallinity, and molecular interactions of a material by measuring the inelastic scattering of light (1). Raman spectroscopy has been employed for the identification of microplastics. Raman analysis not only identifies plastics but also provides profiles of the polymer composition of each sample, similar to FTIR.
To analyze with Raman spectroscopy, the microplastics must be extracted and cleaned from matrices with higher densities, such as sediments by flotation with saturated salt solutions of high density. After cleaning and drying, microplastic particles are mounted on the glass slide or aluminum foil using an adhesive, such as double-sided tape. The mounted microplastics are then analyzed using Raman spectroscopy to obtain information about their chemical composition and structure (2).
When compared to FTIR spectroscopy, Raman techniques offer superior spatial resolution (up to 1 μm as opposed to 10–20 μm in FTIR), a broader range of spectral coverage, heightened sensitivity to non-polar functional groups, and lower water interference, as well as narrower spectral bands. Nevertheless, Raman spectroscopy is vulnerable to fluorescence interference, low signal-to-noise ratio, and the likelihood of sample heating due to the use of a laser light source, which can lead to polymer degradation and background emission (3). However, the different responses and spectra between FTIR and Raman spectroscopy from a microplastic can compromise each other in complex microplastic identification (4).
Ref:
2. M. Bergmann et al. (eds.), Marine Anthropogenic Litter, DOI 10.1007/978-3-319-16510-3_8
3. Catarina F. Araujo, Mariela M. Nolasco, Antonio M.P. Ribeiro, Paulo J.A. Ribeiro-Claro, “Identification of microplastics using Raman spectroscopy: latest developments and future prospects”, Water Research (2018), doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.05.060
4. Won Joon Shin, Sang Hee Hong, and Soen Eo Eo, “Identification methods in microplastic analysis: a review”., Anal. Methods, 2017, 9, 1384
By: Moe Thazin Shwe, SOLEN Research Associate – IPC panel member
Edited by: Hendra WINASTU, SOLEN Principal Associate – IPC panel coordinator
Date: 31 March 2023
Article#: SOLEN-IPC-0014

 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt 日本語
日本語
Pingback: Stereo- (-or Dissecting) Microscopy identification of microplastics - Solen
Pingback: Thermal Analysis for Microplastics Identification - Solen
Pingback: Phân tích các hạt vi nhựa bằng kính hiển vi soi nổi - Solen
Pingback: Combating plastic pollution - Solen
Pingback: Úng phó với ô nhiễm rác thải nhựa - SOLEN