Radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer in the general population, after smoking. Epidemiological studies have provided convincing evidence of a link between indoor radon exposure and lung cancer, even at the relatively low radon levels commonly found in residential buildings. The following article will present what is radon gas? Mechanism of impact and effects of indoor radon on human health
1. What is Radon gas?
Radon is a radioactive gas emitted from rocks and soil that tends to concentrate in enclosed spaces such as mines or houses. Especially, Rn-222 is the product of the radioactive decay chain of uranium-238 (accounting for about 99.3%) . Humans can be exposed to radon mainly by breathing radon in the air that passes through cracks and crevices in buildings and homes. In addition, it is an invisible, odorless, tasteless gas that permeates the ground and diffuses into the air.
The National Cancer Institute defines radon as “a radioactive gas released from the normal decay of the elements uranium, thorium, and radium in rocks and soil.” Radon (222Rn) is a noble gas that is formed from Radium (226Ra) and is the decay product of Uranium (238U) in soil and rocks. Other uranium decay products include the isotopes Thoron (220Rn) and actinon (219Rn). Radon gas, which has a half-life of 3 to 8 days, is emitted from rocks and soil and tends to accumulate in enclosed spaces such as mines or houses. It is a source of ionizing radiation affecting humans and plants and animals on the earth’s surface.
2. Origin of radon
Nguồn ảnh: Internet
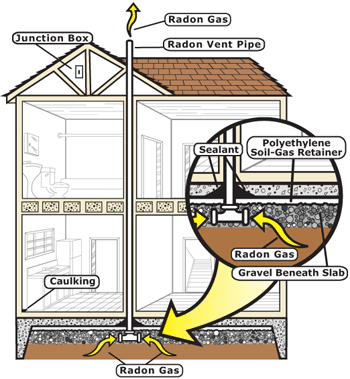
In the 1950s, high concentrations of radon were observed in domestic and drinking water from wells. Initially, concerns about Radon in water focused on the health effects of drinking water. It was later determined that the main risk of radon was from inhalation of radon emitted in the home, and the main cause of gas ingress came from cracks and crevices in buildings and houses. . Other sources such as Radon from building materials, well water contribute less in most cases. According to the U.S. National Radon Program Service, the radon escaped from the soil before becoming trapped under the building’s foundation. Trapped gases build up pressure, which forces them into the building through walls and floors.
3. The change of concentration of Radon . gas

Nguồn: Internet
Radon concentrations in the home vary according to the construction structure of buildings and the ventilation habits of each family’s room. These concentrations not only vary significantly from season to season, but also from day to day and even hour to hour. Because of this variability, estimating annual mean Radon concentrations in indoor air requires reliable measurements of average Radon concentrations for at least three months and preferably longer. Short-term measurements will only provide a rough indication of actual Radon concentrations.
4. Radon's mechanism of action on humans
When Radon gas is inhaled, dense ionized alpha particles emitted from the short-lived decay products of Radon (218 Po and 214 Po) are deposited, which can interact with biological tissue in the lungs leading to to DNA damage. Since even a single alpha particle can cause massive genetic damage to a cell, Radon-related DNA damage can occur at any level of exposure. Therefore, there is no peak concentration threshold that has not yet caused the lung carcinogenicity of Radon.
5. Effects of Radon on Human Health
Nguồn ảnh: Radon Evironmental
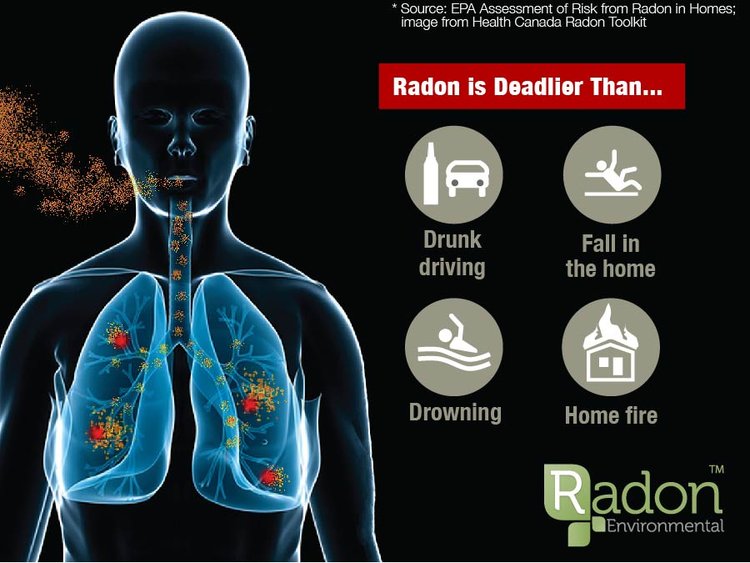
Radon is the second most important cause of lung cancer after smoking in many countries. Radon is more likely to cause lung cancer in smokers or people who have smoked in the past than in lifelong non-smokers due to the strong combined effects of smoking and radon. However, it is the main cause of lung cancer in people who have never smoked.
In the past, investigations into radon gas have focused on underground miners exposed to high concentrations of radon in their occupational environments. However, in the early 1980s, several investigations of radon concentrations in homes and other buildings were carried out. And the results of these investigations, along with research-based risk estimates for mine workers, provide circumstantial evidence that radon may be an important cause of lung cancer in the general population. shared. Later, studies of indoor radon and lung cancer in Europe, North America, and Asia provided strong evidence that radon is associated with lung cancer rates in the general population. Current estimates of radon-related lung cancer rates range from 3% to 14%,
6. Methods to reduce the amount of Radon in the house
Most of the indoor radon is high due to emissions from the floor, radon diffuses out of the ground and into the house. The general method to reduce the amount of Randon in the house is to open the ventilation boxes, windows, etc. so there will be a natural air movement. However, in some cases it is necessary to use mandatory ventilation cells because the house structures are designed on concrete floors, on columns (stilt houses), windows and doors or closed doors. If you are concerned that there may be a problem, contact the Department of Radiation and Nuclear Safety and Control under the Ministry of Science and Technology. Department staff will help you decide what to do. They can advise you on how to check the Radon level in your home, and then, if there is a problem, on how to fix it.


 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt 日本語
日本語