In fact, Food Loss does not have a clear definition. But looking at the overall problem of food waste, we will give some specific definitions and characteristics of Food Loss below.
I. What is Food Loss?
- Food Loss is also known as food loss. It is the reduction in quantity or quality of food due to the decisions and actions of food suppliers in the chain, excluding retailers, food service providers, and consumers (SOFA, 2019).
- According to the High-Level Panel of Experts, Food Loss is a decrease at all stages of the food supply chain before the consumer level in the volume of food originally intended for human consumption.
- FAO defines Food Loss as a reduction in the weight (dry matter) or quality (nutritional value) of food originally produced for human consumption. Most of those losses are due to inefficiencies created in the food supply chain, such as poor logistics and infrastructure, scarcity of technology, knowledge, skills and capacity management of supply chain participants and lack of market access.
II. The difference between Food Loss and Food Waste.
Essentially, Food Waste represents the waste that occurs during the distribution, marketing, and consumption stages. Food Loss represents the loss right before consumption.
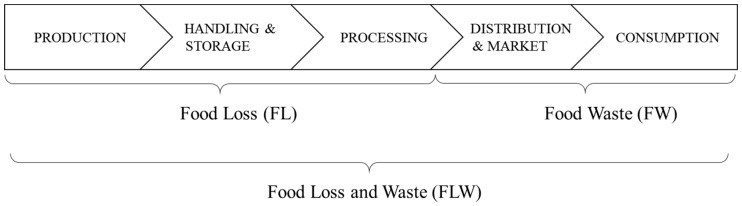
III. Is Food Loss a big problem?
Food Loss occurs in many stages, specifically mentioned as:
- During production;
- During the processing and storage phase;
- During the processing and packaging stage.
Therefore, the amount of food lost depends on a lot of infrastructure, technology and supply chains, etc. This is seen very clearly in developing countries like Vietnam.
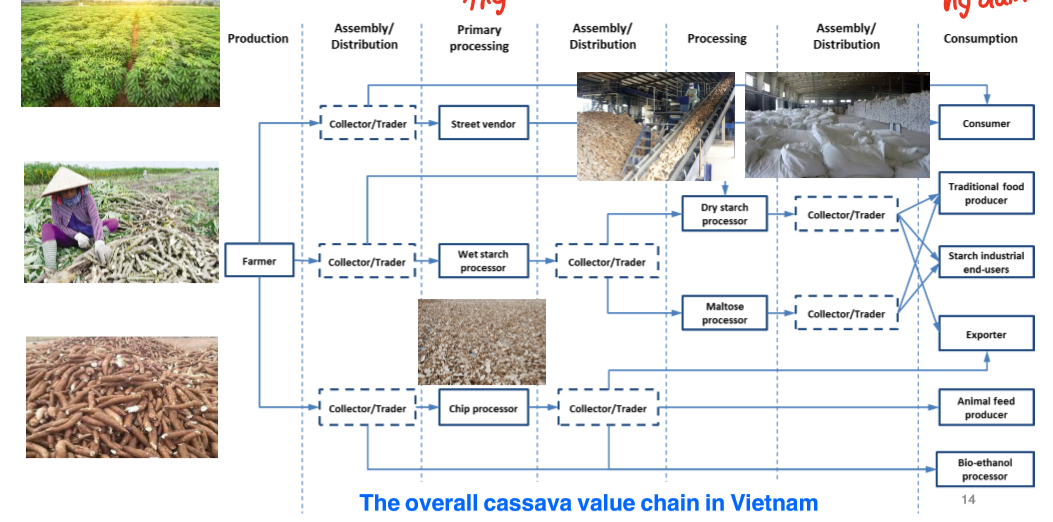
In Vietnam, the value chain is divided. This puts pressure on the government to manage when the legal framework is not yet solid. Leading to a situation where a lot of Food Loss is lost.
What will happen if we do not see this wasteful loss sooner?
- The burden of providing food for 7.6 billion people is expected to increase to 10 billion by 2050;
- The need for better nutrition and lifestyle;
- Resources are constant (soil, water, sunlight) and limited (fossil raw materials);
- Discharging a lot of organic and toxic waste, affecting the environment;
- Challenges in ensuring security-quality-safety-environment.
[REFERENCE]
- Rovshen Ishangulyyev, Sanghyo Kim, Sang Hyeon Lee 3. Understanding Food Loss and Waste—Why Are We Losing and Wasting Food? 2019. National Library of Medicine. doi: 10.3390/foods8080297;
- To Kim Anh. Food Loss and Food Waste Vietnam case. 2023. Summer school in Circular Economy.


 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt 日本語
日本語