Introduction
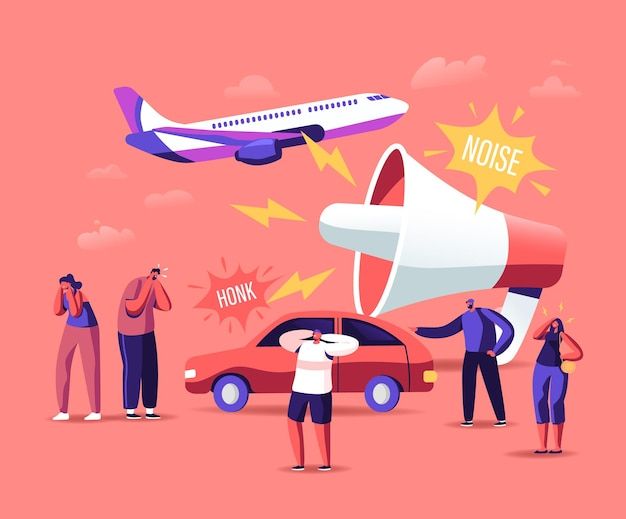
Noise pollution is defined as the distressing noise that may harm the physical/mental activity of human being as well as animal life. Nowadays the matter of noise pollution is of prime concern. The objective of the presented paper is to create social awareness among the educated people and spread the knowledgeable information about the noise pollution. Noise is found almost everywhere. Some industrial locations have even louder continuous noise. Community noise is chiefly produced by transportation sources, most often airplanes and highway vehicles. Noise sources are also in public buildings and residences.
Classes of Noise Related to Noise Pollution
Noise is unwanted sound which is emitted by a vibrating body and on reaching the human ear causes the feeling of hearing through nerves. Sounds produced by all vibrating bodies are not audible. The limits of audibility are from 20 Hz to 20 kHz. Sounds of frequencies less than 20 Hz are called infrasonics and greater than 20kHz are called ultrasonics.
- Atmospheric noise: It is a kind of radio noise caused by natural atmospheric processes, chiefly lightning discharges in thunderstorms. On a worldwide scale, 3.5 million lightning flashes occur daily.
- Environmental noise: It is the abstract of noise pollution from outside sources, caused mainly by transport systems which includes a wheeled passenger vehicle that carries its own motor and various recreational activities. This class of noise is generally present in some form in all areas of human activity. The effects in humans of exposure to environmental noise may vary from emotional to physiological and psychological. The effects of environmental noise in humans may vary from emotional to physiological and psychological. Low level noise is not necessarily harmful. However, the undesirable effects of noise exposure could include annoyance, sleep disturbance, nervousness, hearing loss and stress-related problems. Noise from transportation is generated by the engine/exhaust and aerodynamic noise compression and friction in the air around the body during motion. Recreational noise could be generated by a large number of different sources and processes. The background noise like alarms, people talking, bioacoustic noise from animals also constitute the environmental noise.
- Noise which affects workers in the course of their jobs and is due to the work environment and/or to the machinery which they must operate. Industrial noise varies in loudness, frequency components, and uniformity. It may be roughly uniform in frequency response and constant in level.
Technical Terms with Noise Pollution
The definition of some important technical terms related with noise pollution measuring parameters and indicators is quoted from American National Standards Institute (ANSI) standard.
- Audiogram: Graph of hearing threshold level as a function of frequency. Sounds of frequencies less than 20 Hz are called infrasonics and greater than 20,000 Hz are called ultrasonics.
- Baseline Audiogram: It is the audiogram against which subsequent audiograms will be compared for the estimate of significant threshold shift. It is obtained from an audiometric examination administered before employment or within the first 30 days of employment that is preceded by a period of at least 12 hours of silence.
- Continuous Noise: Noise with negligibly small fluctuations of level within the period of observation.
- Crest factor: 10 times the logarithm to the base 10 of the square of wideband peak amplitude of a signal to the time-mean-square amplitude over a stated time period.
- Decible, A-weighted (dBA): The sound level measured with the A-weighting network on a sound level meter.
- Decibel, C-weighted (dBC): The sound level measured with the C-weighting network on a sound level meter.
- Noise reduction rating (NRR): It indicates a hearing protector’s noise reduction capabilities (in dB), is a single number rating that is required by law to be shown on the label of each hearing protector sold in the USA.
- Derate: To use a fraction of a hearing protector’s NRR to calculate the noise exposure of the worker wearing that protector.
References
Govt. Engineering College Ajmer (Raj.), N. B. (2016). Noise Pollution: A Review. Journal of Environment Pollution and Human Health,, Vol. 4, No. 3, 72-77.


 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt 日本語
日本語