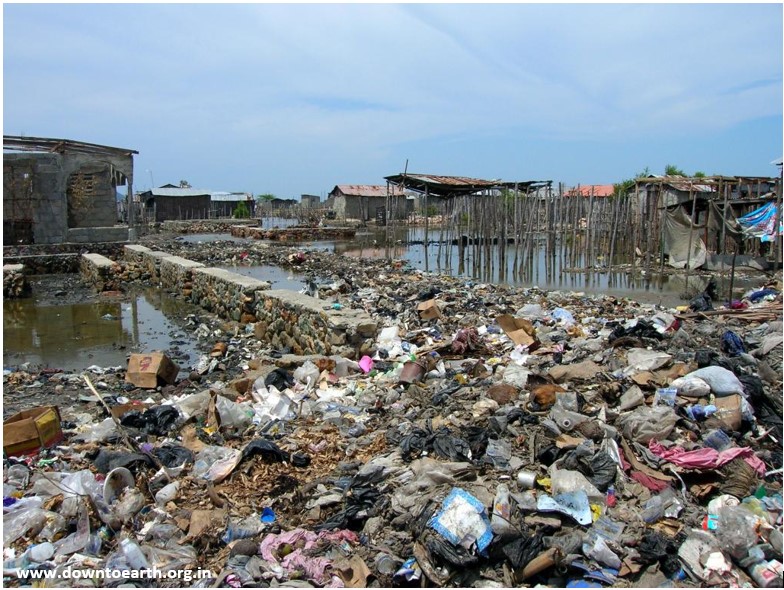
“Solid waste” means any garbage or refuse, sludge from any wastewater treatment facilities, and other discarded material from industrial, commercial, mining, agricultural operations, as well as community activities (1). In 2020, the world was estimated to generate 2.24 billion tons of solid waste, amounting to a footprint of 0.79 kilograms per person per day (2). Disposal of solid wastes is a stinging and widespread problem in both urban and rural areas in many developed and developing countries. Improper disposal of solid wastes can lead to adverse health and environmental outcomes, for example through water, soil and air contamination (3).
Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) or commonly known as trash or garbage comes from our homes, schools, hospitals and business consists of everyday items we use and then throw away, such as product packaging, grass clippings, furniture, clothing, bottles, food scraps, newspapers, appliances, paint, and batteries (4). Industrial solid waste is defined as waste generated by manufacturing or industrial processes. The industrial solid waste includes cafeteria garbage, dirt and gravel, masonry and concrete, scrap metals, weed grass and trees, wood and scrap lumber and similar wastes (5). Agricultural solid waste is defined as waste produced from various agricultural operations. The agricultural solid waste includes manure and other wastes from farms, poultry houses and slaughterhouses; harvest waste; that enter into water, air or soils; and salt and silt drained from fields (6). Depending on the condition of the wastes to the environment, they also can be distinguished into hazardous and non-hazardous waste.
Stay tuned for the next article about hazardous and non-hazardous waste!
Ref:
1. https://www.epa.gov/hw/criteria-definition-solid-waste-and-solid-and-hazardous-waste-exclusions
2. https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/urbandevelopment/brief/solid-waste-management
3. https://www.who.int/tools/compendium-on-health-and-environment/solid-waste
4. https://archive.epa.gov/epawaste/nonhaz/municipal/web/html/
5. https://www.safewater.org/fact-sheets-1/2017/1/23/industrial-waste
6. https://stats.oecd.org/glossary/detail.asp?ID=77
By: Moe Thazin Shwe, SOLEN Research Associate – IPC panel member
Edited by: Hendra WINASTU, SOLEN Principal Associate – IPC panel coordinator
Date: 6 December 2022
Article#: SOLEN-IPC-0005
The Former Article: https://solenvn.com/en/different-types-of-micro-plastics/
The Latter Article: https://solenvn.com/en/biodegradable-plastics/


 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt 日本語
日本語
Pingback: Biodegradable Plastics - Solen
Pingback: Different types of micro plastics - SOLEN-IPC-004 - Solen